AI, or artificial intelligence, enables machines to mimic human intelligence, like learning, reasoning, solving problems, and understanding language. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is reshaping the landscape of patient care, ushering in a new era of precision, efficiency, and accessibility in healthcare. From enhancing diagnostic accuracy to personalizing treatment plans and streamlining administrative processes, AI is revolutionizing the way care is delivered. With its ability to analyze vast amounts of medical data and uncover patterns that might elude even the most experienced practitioners, AI is driving advancements that were once considered science fiction (Sci-Fi); AI is now revolutionizing patient care in a big way. This transformation promises not only to improve health outcomes but also to empower healthcare professionals and patients alike, setting the stage for a healthier, more connected future.
AI in Nursing care
Studies suggest that nurses dedicate about 25% of their 12-hour shifts to indirect care, with documentation being a major component. Another study found that nurses spend approximately three hours per shift on tasks like documenting orders and coordinating care. AI is transforming nursing care by automating routine tasks like documentation and scheduling, freeing up time for direct patient care. Additionally, AI fosters collaboration among healthcare teams by streamlining data sharing and communication.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural Language Processing (NLP) has significantly advanced patient care by transforming how healthcare providers interact with data and patients. For example, NLP tools can analyze unstructured medical records such as scribbled physician’s notes to extract critical information, enabling faster and more accurate diagnoses. They also assist in clinical decision-making by identifying patterns in patient data that might otherwise go unnoticed. Additionally, NLP-powered chatbots and virtual assistants improve communication by answering patient queries and providing timely information. These applications not only enhance efficiency but also contribute to more personalized and effective care.
Clinical decision support systems (CDSS)
AI-powered tools, such as clinical decision support systems and predictive analytics, assist nurses in making more informed decisions and identifying patients at risk (e.g. of falls and catheter-associated urinary tract infections) enabling proactive interventions.
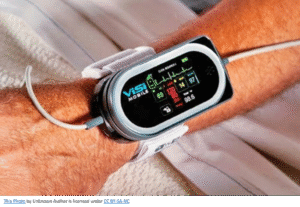
Remote monitoring devices
Smart wearables, like ECG monitors and blood pressure trackers, enable continuous patient monitoring, alerting nurses to any abnormalities in real-time ensuring timely interventions. Additionally, AI enhances remote patient monitoring, reducing the need for frequent hospital visits while ensuring patients receive consistent care.
Generative AI
Gen’ AI, can be utilized for creating personalized care plans by analyzing patient data, including lab results and medical images, to provide accurate diagnoses and recommendations helping nurses tailor treatments to individual needs. Generative AI simplifies medical jargon, improving communication between nurses and patients while fostering trust and understanding.
Generative AI enhances patient education by creating personalized content tailored to individual conditions, symptoms, and questions. It simplifies complex medical concepts with visual aids and enables interactive learning experiences through Q&A dialogues. AI also offers reminders, improves health literacy at different reading levels, supports mental health, and provides information in multiple languages, ensuring accessible and effective care.
Robotics and Automation
Robotic assistants are also being used to transport supplies, deliver medications, and even assist with patient mobility. Automation technologies are making a big impact in nursing care. For example, smart infusion pumps ensure accurate medication delivery, reducing errors and improving patient safety.
Laying the groundwork for responsible AI integration in patient care
The use of AI in nursing care contributes to enhancing efficiency, reducing burnout, and improving patient outcomes. However, to effectively integrate AI into healthcare, organizations must focus on building strong data infrastructure and fostering AI talent while promoting a data-driven culture. Equally important is the development of ethical guidelines that address concerns like bias, fairness, and privacy, ensuring alignment with healthcare values. Advancing interoperability and standardization across the industry is crucial for seamless data sharing and collaboration.
Engaging with regulatory bodies to establish AI governance frameworks that prioritize both innovation and patient safety is vital. Additionally, organizations should adopt systems for continuous monitoring and improvement of AI models, ensuring they remain effective and adaptable in the rapidly evolving healthcare landscape. Together, these steps lay the groundwork for responsible and impactful AI integration.
What’s your opinion?
Do you think AI will replace physicians and nurses in future?
Would you like technology to replace humans in healthcare?