Nurses and physicians face several challenges in clinical practice, from staffing shortages that lead to increased workloads and burnout, to administrative tasks that reduce time for patient care. Exposure to infectious diseases and physical strain add to workplace safety concerns, furthering the stress. Communication barriers often hinder interprofessional collaboration, which impacts patient outcomes. Besides, the lack of mental health support exacerbates stress and burnout, while diversity and inclusion issues in the workforce can create a less cohesive environment. Artificial Intelligence (AI) utilization benefits Healthcare in multiple ways. Introducing artificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare can optimize staffing, reduce burnout, and enhance patient care, addressing these challenges to create a more supportive environment for healthcare professionals. This blog post explores the potential of AI in addressing these critical challenges and highlights success stories from healthcare organizations that have embraced AI technologies.
- AI Solutions for Clinical Practice: AI integration optimizes healthcare services
- Resources for Implementing AI in Healthcare to Manage Employee Shortages, Exhaustion, and Healthcare Delivery Challenges
- Potential barriers to utilizing AI Healthcare
- Integrating Artificial intelligence (AI) in Healthcare: Balancing Opportunity Costs
- Potential Return on Investment: Artificial Intelligence (AI) utilization benefits Healthcare
- The Average Cost for Various AI Solutions in Healthcare
- Strategies for Reducing Costs in AI Healthcare Project Implementation
- Some success stories of AI application enhancing healthcare
- Key Stakeholders for AI deployment to boost healthcare outcomes
- Conclusion

AI Solutions for Clinical Practice: AI integration optimizes healthcare services
Solutions from Artificial Intelligence (AI) utilization can benefits Healthcare in several aspects. Integrating AI into clinical practice addresses challenges faced by nurses and physicians. Artificial intelligence (AI) optimizes staffing levels through predictive analytics, ensuring adequate workforce planning and reducing burnout. Automated documentation and advanced EHR systems minimize administrative burdens, allowing healthcare professionals to focus on patient care. AI-driven safety protocols enhance workplace safety by identifying potential risks and suggesting preventive measures.
AI-powered communication tools foster interprofessional collaboration, improving teamwork and patient outcomes. Additionally, AI such as the smart rings supports mental health and well-being by monitoring stress levels and providing early intervention. Overall, AI integration creates a more efficient, safe, and supportive healthcare environment.
Resources for Implementing AI in Healthcare to Manage Employee Shortages, Exhaustion, and Healthcare Delivery Challenges
To effectively implement Artificial intelligence (AI) solutions in healthcare, several resources are necessary:
- Advanced EHR Systems: Integrate AI with existing workflows to reduce administrative burdens effectively. This approach streamlines tasks and frees up healthcare professionals to focus more on patient care.
- Cloud-Based AI Services: Offer scalable infrastructure and data storage solutions.
- Training Programs: Upskill staff on using AI tools and technologies effectively.
- Predictive Analytics Software: Optimize staffing levels and resource allocation.
- AI-Powered Communication Tools: Enhance collaboration among healthcare teams.
- Mental Health Support Platforms: Monitor and address stress and burnout in real time.
- Safety Protocol Systems: Identify and mitigate workplace risks efficiently. By leveraging these resources, healthcare organizations can enhance efficiency, reduce burnout, and improve patient care.
Potential barriers to utilizing AI Healthcare
- Data Privacy and Security: Ensuring patient data privacy and security is a significant challenge. Robust measures are required to protect sensitive information. Healthcare providers must navigate FDA regulations to get approvals for AI-based diagnostic tools, which can be complex and time-consuming.
- Regulatory and Legal Issues: Navigating complex regulations and legal requirements can delay AI implementation. Healthcare providers must navigate FDA regulations to get approvals for AI-based diagnostic tools, which can be complex and time-consuming.
- Integration with Existing Systems: AI solutions must seamlessly integrate with existing electronic health record (EHR) systems and workflows. Integrating AI-driven decision support systems with existing EHRs requires significant effort to ensure seamless data flow and interoperability
- Bias and Fairness: AI algorithms may exhibit biases, leading to unequal treatment and outcomes. Hospitals must continuously monitor and update AI algorithms to prevent biases and ensure fair treatment across demographics.
- Cost and Resource Constraints: Implementing AI requires significant financial investment and resources. Small clinics wanting to adopt AI for administrative tasks need to explore cost-effective AI solutions and seek grants to overcome budget constraints.
- Lack of Trust and Acceptance: Healthcare professionals may be skeptical of AI’s reliability and effectiveness. Providing training and demonstrating AI’s effectiveness can build trust.
- Skill Gaps: Training and upskilling staff to use AI tools effectively can be challenging.
Addressing these barriers requires a comprehensive approach, including collaboration between healthcare organizations, policymakers, and technology developers. Hospitals implementing AI for patient care optimization must invest in training and hire skilled professionals to address the lack of AI expertise.
Integrating Artificial intelligence (AI) in Healthcare: Balancing Opportunity Costs
The opportunity cost of Artificial Intelligence (AI) utilization in healthcare involves potential benefits and resources that could be allocated elsewhere. Moreso, AI has the potential to revolutionize healthcare. However, weighing the opportunity costs is essential to ensure the benefits outweigh any potential drawbacks. Here are some key aspects to consider:
- Financial Investment: AI implementation requires significant financial resources, which could alternatively be invested in hiring more healthcare staff, upgrading medical equipment, or expanding facilities.
- Time and Effort: Developing and integrating AI systems demands time and effort, potentially diverting attention from other critical projects that might offer immediate benefits for patient care.
- Training and Skill Development: Training healthcare professionals to use AI tools effectively requires time and resources, which could be allocated to other training programs or professional development opportunities.
- Ethical and Legal Considerations: Addressing ethical and legal challenges related to AI can be complex and time-consuming, delaying other important policy or regulatory initiatives.
- Potential for Inequity: Focusing on AI may lead to disparities in healthcare access, especially in underserved or rural areas lacking technological infrastructure. These resources could address such disparities instead.
- Risk of Failure: AI projects might not always deliver expected benefits, and resources invested in these projects could be seen as wasted if goals are not achieved.
Potential Return on Investment: Artificial Intelligence (AI) utilization benefits Healthcare
The expected return on investment (ROI) of AI in healthcare can vary based on the specific application and implementation. However, several studies and reports highlight its potential benefits:
- 1. Operational Efficiency: AI can significantly improve operational efficiency by automating routine tasks, optimizing resource allocation, and reducing administrative burdens. For example, AI-powered automation could free up 13% to 21% of nurses’ time, translating to an additional 240 to 400 hours per nurse per year.
- 2. Cost Savings: AI can help reduce costs by streamlining operations, minimizing unnecessary delays, and optimizing bed management. Hospitals can operate more efficiently, managing higher patient volumes without additional infrastructure investments.
- 3. Improved Patient Outcomes: AI can enhance patient care by enabling faster access to care, reducing wait times, and supporting more accurate discharge planning. These improvements contribute to better health outcomes and higher patient satisfaction.
- 4. Predictive Analytics: AI can provide predictive analytics to anticipate patient needs, optimize staffing levels, and improve patient flow. This can lead to shorter hospital stays, lower operational costs, and increased bed availability.
- 5. Enhanced Patient Engagement: AI-powered digital platforms, patient portals, and virtual care options can improve patient engagement and experience. This can lead to better adherence to treatment plans and improved health outcomes.
While the exact ROI can vary, many healthcare organizations have reported moderate to significant returns on their AI investments. For example, more than 40% of C-suite executives surveyed by Deloitte reported a moderate to significant return on their AI investments.
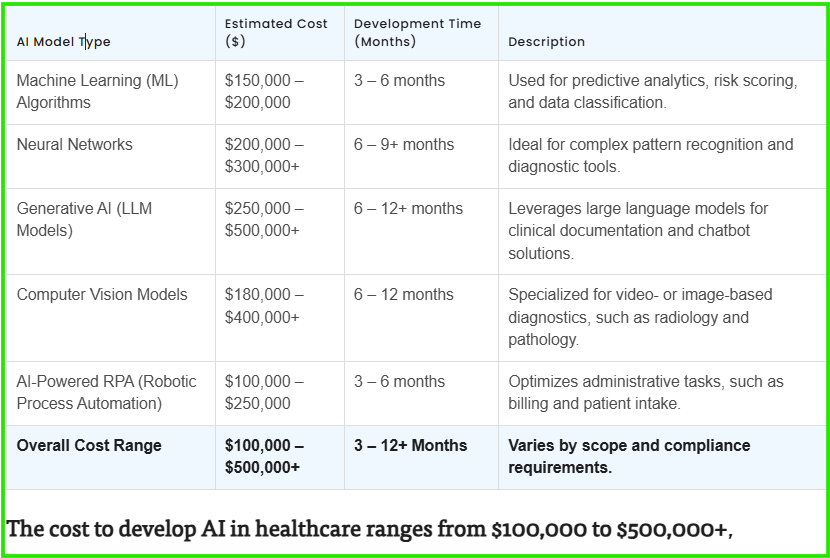
The Average Cost for Various AI Solutions in Healthcare
The cost of implementing an AI project in healthcare can vary widely depending on the complexity and scope of the project. Based on information topflight, here are some estimated costs for different types of AI solutions in 2025.
Strategies for Reducing Costs in AI Healthcare Project Implementation
By implementing the following strategies, healthcare organizations can optimize their AI project budgets and achieve cost-effective solutions while maintaining high standards of quality and innovation. These are:
- Strategic Planning: Develop a clear roadmap outlining project objectives, scope, and milestones. Early planning helps identify cost-saving opportunities and prevent resource wastage.
- Smart Resource Allocation: Assign roles based on team expertise and encourage cross-functional collaboration to enhance innovation and reduce redundant efforts.
- Open-Source Tools: Utilize open-source AI tools and frameworks to cut software and infrastructure expenses. These tools provide robust solutions without the high costs associated with proprietary software.
- Cloud-Based Solutions: Leverage cloud-based AI services to reduce the need for expensive on-premises hardware. Cloud solutions offer scalability and flexibility, allowing you to pay only for the resources you use.
- Pilot Projects: Start with small pilot projects to test AI solutions before full-scale implementation. This approach helps identify potential issues and optimize the solution without significant upfront investment.
- Vendor Partnerships: Collaborate with technology vendors and partners who can provide AI solutions at a lower cost. Negotiating favorable terms and leveraging vendor expertise can lead to cost savings.
- Continuous Monitoring and Optimization: Regularly monitor AI project performance and costs. Use data-driven insights to optimize resource allocation and make adjustments as needed to stay within budget.
- Training and Upskilling: Invest in training programs to upskill existing staff in AI technologies. This reduces the need for hiring external experts and ensures that your team can effectively manage AI projects.
- Automated Cost Estimation: Use AI-powered tools to automate project cost estimation and improve budgeting accuracy. These tools analyze historical data and provide precise cost predictions, reducing the risk of budget overruns.
- Efficient Data Management: Implement efficient data management practices to reduce storage and processing costs. This includes data cleaning, compression, and using cost-effective storage solutions.
Some success stories of AI application enhancing healthcare
- Cleveland Clinic: Optimizing Patient Flow:
- Cleveland Clinic implemented AI to improve patient flow and reduce wait times. Using predictive analytics, they identified bottlenecks in real time, enabling staff to allocate resources more efficiently. Result: A significant reduction in patient wait-times and enhanced operational efficiency.
- Mayo Clinic: Advancing Diagnostics with AI:
- Mayo Clinic integrated AI tools to assist in diagnosing heart disease and certain types of cancer. By analyzing imaging data and patient records, AI algorithms identified patterns that might be missed by human eyes. Result: Improved diagnostic accuracy and earlier detection, leading to better patient outcomes.
- Stanford Medicine: Combating Provider Burnout:
- Stanford Medicine introduced AI to reduce provider burnout by automating administrative tasks like note-taking and appointment scheduling. These tools also streamlined communication between patients and providers. Result: Improved provider satisfaction and more time for patient care.
- Kaiser Permanente: Personalized Care with Predictive Analytics:
- Kaiser Permanente leveraged AI to create predictive models that identify patients at risk of chronic conditions. These models guided early interventions and personalized care plans. Result: Reduced hospital admissions and better management of chronic diseases.
- TidalHealth Peninsula Regional: Clinical Decision Support:
- TidalHealth Peninsula Regional partnered with IBM to implement IBM Micromedex with Watson, a clinical decision support software. This AI solution combined clinical decision support and AI with patients’ electronic medical records, making it easier to find relevant and useful information. Result: Reduced time spent on clinical searches, allowing more time for patient care.
Key Stakeholders for AI deployment to boost healthcare outcomes
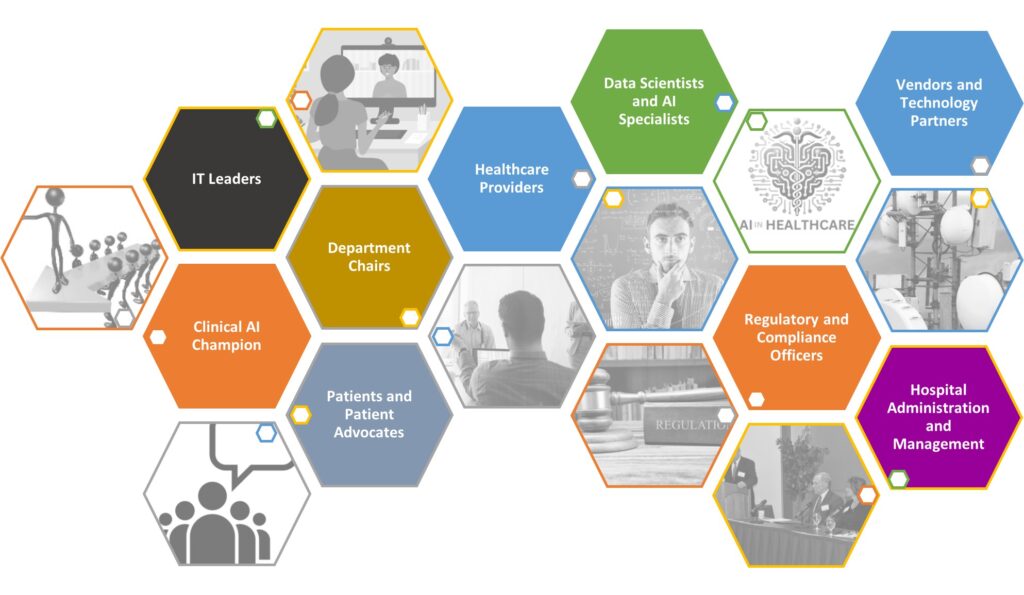
Executing a clinical or hospital AI integration project involves several key stakeholders, each playing a crucial role in the successful implementation and adoption of AI technologies. The Clinical AI Champion drives the organization’s AI strategy, advocating for AI adoption and aligning it with clinical goals. Department Chairs and Vice Chairs provide guidance and support for AI initiatives within their service lines. IT Leaders manage the technical aspects of AI integration, including infrastructure, data management, and cybersecurity. Healthcare Providers, such as physicians, nurses, and allied health professionals, offer valuable insights into the practical application and effectiveness of AI in clinical settings. Data Scientists and AI Specialists develop, train, and validate AI models, ensuring accuracy, reliability, and ethical standards.
Regulatory and Compliance Officers ensure AI implementations comply with healthcare regulations and address legal and ethical concerns. Patients and Patient Advocates provide essential feedback and perspectives for designing patient-centered AI solutions that improve care quality and outcomes. Hospital Administration and Management offer strategic direction, allocate resources, and oversee the overall implementation of AI projects. Vendors and Technology Partners collaborate with healthcare organizations to provide AI solutions, technical support, and ongoing maintenance. These stakeholders must work together to ensure the successful integration of AI technologies in clinical and hospital settings, ultimately enhancing patient care and operational efficiency.
Conclusion
Integrating Artificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare offers transformative solutions to optimize staffing, reduce burnout, and enhance patient care. By embracing AI, healthcare organizations can create efficient, safe, and supportive environments for nurses and physicians, ultimately improving patient outcomes and addressing critical challenges in the healthcare system. The future of healthcare is AI-powered.